-
210630_1(Spring)Spring 2021. 6. 30. 18:30
@aspectj + String => AOP
xml 사용이 줄어든다.
aspect = pointcut + advice
advisor = pointcut + advice
package test.aspectj.spring.aop; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; @Aspect public class MannerAOP { @Before("execution(* set*(String))") public void confirmName() { System.out.println("이름을 세팅합니다."); } @Before("execution(* set*(java.util.GregorianCalendar))") public void confirmBirthday() { System.out.println("생일을 세팅합니다."); } @Before("execution(* set*(int))") public void copfirmAge() { System.out.println("나이를 세팅하기 전입니다."); } @After("execution(* set*(int))") public void confirmAge2(){ System.out.println("나이를 세팅하기 이후입니다."); } @Before("execution(* getAge(..))") public void confirmBeforeSettingAge1() { System.out.println("나이를 반환하기 이전입니다."); } @AfterReturning(returning="age", value="execution(* getAge(..))") public void confirmBeforeSettingAge2(int age) { System.out.println("나이를 반환된 나이입니다 1:" +age); } @After("execution(* getAge(..))") public void confrimBeforeSettingAge123() { System.out.println("반환된 반환된 나이입니다2:"); } @AfterReturning(returning = "name", value = "execution(* getName(..))") public void confirmBeforeSettingName2222(String name) { System.out.println("원래 이름은 :" + name); } @AfterReturning(returning = "date", value="execution(* getBirthday(..))") public void confirmBeforeSettingDate3333(GregorianCalendar date) { System.out.println("원래 생일은 : " +date.getTime()); } }package test.aspectj.spring.aop; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; public interface Hero { public int getAge(); public void setAge(int age); public GregorianCalendar getBirthday(); public void setBirthday(GregorianCalendar birthday); public String getName(); public void setName(String name); }package test.aspectj.spring.aop; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; public class JangGilSan implements Hero { String name; int age; GregorianCalendar birthday; private JangGilSan() { name="장길산"; age = 16; birthday= new GregorianCalendar(1588, 7, 15); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { System.out.println("나이를 반환 하고 있는데~"); return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; System.out.println("나이가 세팅되고 있습니다."); } public GregorianCalendar getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(GregorianCalendar birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Override public String toString() { return "Name:"+name+"\nAge :" +age+ "\nBirthday:"+birthday.getTime(); } }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 자동으로 설정함 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <bean id="jgs" class="test.aspectj.spring.aop.JangGilSan"/> <bean id="mannerOAP" class="test.aspectj.spring.aop.MannerAOP"/> </beans>package test.aspectj.spring.aop; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestFirstAOP { public static void main(String[] agrs) { BeanFactory bf = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("test/aspectj/spring/aop/aopAppContext.xml"); Hero human = (Hero) bf.getBean("jgs"); System.out.println("나이를 처리후 화면에 리턴된 나이입니다" + human.getAge()); System.out.println(human.getBirthday().getTime()); System.out.println(human.getName()); human.setAge(35); human.setBirthday(new GregorianCalendar(1669, 7, 15)); human.setName("이순신"); System.out.println(human); } }
4) @aspectj + Spring => AOP
xml 사용이 줄어든다
5) @aspectj + Spring => AOP
지정자가 다름 this() within()
실행시 : aspectj 적용을 해제하고 실행, lib가 없는경우 maven에서 따다가 pom.xml에 넣는다(주의. 버전을 맞춰야한다)
AOP: 관점 지향 프로그램 - 이론
실무적 -- 구체적인 방법
aspect ==> pointcut + advice
before, after return, atter whrow, after, around
지정자가 다름 this(인터페이스) within(클래스||클래스2||클래스3)
인터페이스라 -> 실행시 : aspectj 적용을 해제 하고 실행, lib가 없는 경우
결과는 ---
Dog
Cat <--- dog와 cat은 생성자에서
<--- before를 적용했다면
빙고 <--- 포인트컷 지정 메서드 내부 출력문
안녕 <--- after return, after throws 둘중 하나가 나옴
<--- after를 적용했다면
톰
안녕
package test.aspectj.aop.animal; public interface Animal { void getName(); }package test.aspectj.aop.animal; public class Dog implements Animal { public Dog() { System.out.println("Dog"); } @Override public void getName() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("빙고"); } }package test.aspectj.aop.animal; public class Cat implements Animal { public Cat() { System.out.println("Cat"); } @Override public void getName() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("톰"); } }package test.aspectj.aop.animal; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Aspect public class MannerAOP { //포인트 컷 지정 함 //Human은 인터페이스이므로 생성자를 사용못하므로 //this 키워드를 사용한다 // 그 클래스에 있는 메소드가 실행되는 시점들(join point)을 포인트 컷으로 @Pointcut("this(Animal)") public void sayGoodBye() { //바디가 비어야 함 } //@Pointcut("within(Dog) || within(Cat)") //public void sayGoodBye() {} //는 @Pointcut("this(Animal)")결과와 동일 합니다. @AfterReturning("sayGoodBye()") public void say() { System.out.println("안녕이라고요~"); } }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> <bean id="dog" class="test.aspectj.aop.animal.Dog"/> <bean id="cat" class="test.aspectj.aop.animal.Cat"/> <bean id="mannerAOP" class="test.aspectj.aop.animal.MannerAOP"/> </beans>package test.aspectj.aop.animal; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AnimalNameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub BeanFactory bf = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("test/aspectj/aop/animal/aopAppContext.xml"); Animal animal = (Animal) bf.getBean("dog"); animal.getName(); animal = (Animal) bf.getBean("cat"); animal.getName(); } }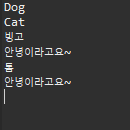
6) aspectj + Spring => AOP
- DI가 나옴,
- @around <== before인지 after인지 코딩시 지정할 수 있다.
<bean id ='xxx' class="MyClass">
<param name='abc'>
</bean>
DI--->MyClass에는 abc변수가 존재해야 하고, abc해당 setter가 존재해야한다.
스프링이 인스턴스를 생성하여 그 인스턴스를 타겟클래스에 주입한다 <== 개념
따라서 의존성을 낮추는 방향으로 프로그램한다.
처리법 : 주입되는 것을 받으려면 해당 인스턴스 변수와 setter가 필요하다. <== 중요 기능
package test.aspectj.spring.di.fish; public interface Fish { String getName(); void setName(String name); //DI를 사용하기위한 변수하나와 세터를 준비한다. }package test.aspectj.spring.di.fish; public class Fishlmpl implements Fish { private String name; @Override public String getName() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("게터동작"); return name; } @Override public void setName(String name) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("세터동작"); this.name = name; } }package test.aspectj.spring.di.fish; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Aspect public class FishAspect { @Pointcut("execution(* get*(..))") public void sayHi() { //여기서는 출력문을 넣을 수 없음 } // @Around("sayHi()") public Object say(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)throws Throwable{ System.out.println("전에 동작함"); Object name = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("후에 동작함"); return name; } // @Around("execution(* set*(..))") public void validate(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)throws Throwable{ System.out.println("setXXX 에서 동작함"); //pjp.proceed(new Object[]{"고~래!"}); //위처럼 객체를 변결 할 수 도 있다. pjp.proceed(); } }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!-- this is the object that will be proxied by Spring's AOP infrastructure --> <bean name="gamulchi" class="test.aspectj.spring.di.fish.Fishlmpl"> <property name="name" value="가물치"/> </bean> <bean name="gumbung" class="test.aspectj.spring.di.fish.Fishlmpl"> <property name="name" value="금붕어"/> </bean> <!-- this is the actual advice itself --> <bean id="fishAspect" class="test.aspectj.spring.di.fish.FishAspect"/> </beans>package test.aspectj.spring.di.fish; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class FishNameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub BeanFactory bf = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("test/aspectj/spring/di/fish/aopAppContext.xml"); Fish fish1 = (Fish) bf.getBean("gamulchi"); //Fish fish2 = (Fish) bf.getBean("gumbung"); System.out.println("이름1:"+fish1.getName()); //System.out.println("이름2:"+fish2.getName()); fish1.setName("가물가물~"); //fish2.setName("금붕금붕~"); System.out.println("바뀐이름1:"+fish1.getName()); //System.out.println("바뀐이름2:"+fish2.getName()); } }
다른소스에 DI AOP 적용하는 연습
1.공유자료중, chapter1.war를 다운로드한다.
2.이클립스에서 import한다.
3.연동문구를 확인한다. -->설정한다. <--- 잘들여다보면 배웠던 내용이 들어 있다.
4.로그인을 해본다.
chapter1
<!-- 1. 주의 : mysql 드라이버 톰캣 밑에 넣을것 / mysql-connecter는 최신1.5x버젼사용할것 2. server.xml에서 <Resource auth="Container" name="jdbc/SpringDS" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" password="1234" maxIdle="2" maxWait="5000" username="javauser" url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/javadb" maxActive="4"/> 3. server.xml의 맨밑 Context 설정에서 <ResourceLink name="jdbc/SpringDS" type="javax.sql.DataSource" global="jdbc/SpringDS" /> 4. web.xml 에서 <resource-ref> <description>DB Connection</description> <res-ref-name>jdbc/SpringDS</res-ref-name> <res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type> <res-auth>Container</res-auth> </resource-ref> -->5.로그인 과정을 구조를 분석한다.
1) login.jsp <--뷰
id/pw 전송폼
2) userid와 passwd를 가지고
login_action.jsp으로 이동 <--- 컨트롤
3) NonUserService클래스의 login(userId, password); 와
findUser(userId); 함수가 관여하고있다. <--DTO
4) UserDAOFactory 의 getUserDAO 메소드실행 -- DB종류확인한다(mysql이면 mysql로 dao전송) <--Factory
5) MySQLUserDAO <--DAO
User findUser(String userId) -- select sql 문장
분석목적
DI, AOP를 적용 할 것이다.
1단계 - DI를 어떻게 적용할까
web.xml --- 스프링을 웹어플에 적용한다.
filter는 servlet보다 우선적으로 호출된다.
그래서 기술도 servlet보다 먼저 해야 한다.
listener : 톰캣이 실행할때 스프링이 응답할수 있도록 context-param을 읽어서 준비하고 대기한다.
context-param : 스프링이 구동될때 사용하는 기본적인 파라미터정보를 기술한다.
결국 , 요청--->filter ---> listner--->servlet 순으로 전달된다.
welcome-file-list : 기술된 파일이 존재하면 파일명이없을때 자동으로 응답하게 된다.
----lib는 추가할 것이 하나도 없다.
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
210706_1(iBatis) (0) 2021.07.06 210705_2(iBatis) (0) 2021.07.05 210702_1(Spring) (0) 2021.07.02 210701_1(Spring_DI적용하기) (0) 2021.07.01 210629_1(Spring) (0) 2021.06.29